Matchless Info About Balance Sheet Approach Bad Debt

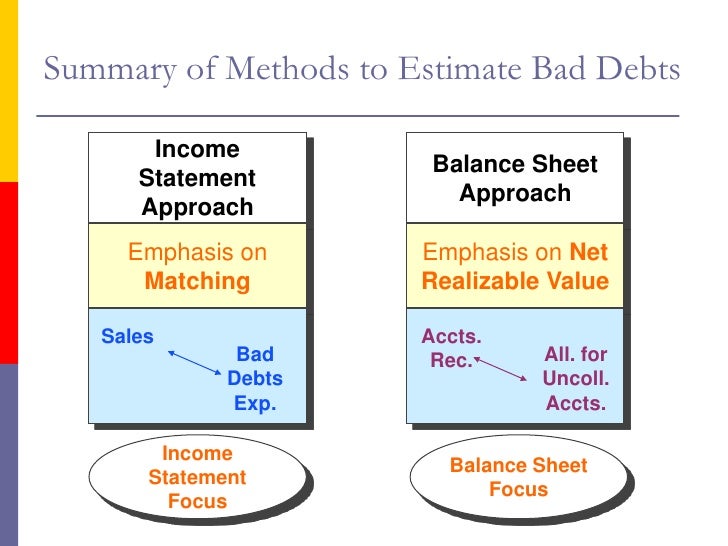
The percentage sales method and the accounts receivable aging method.
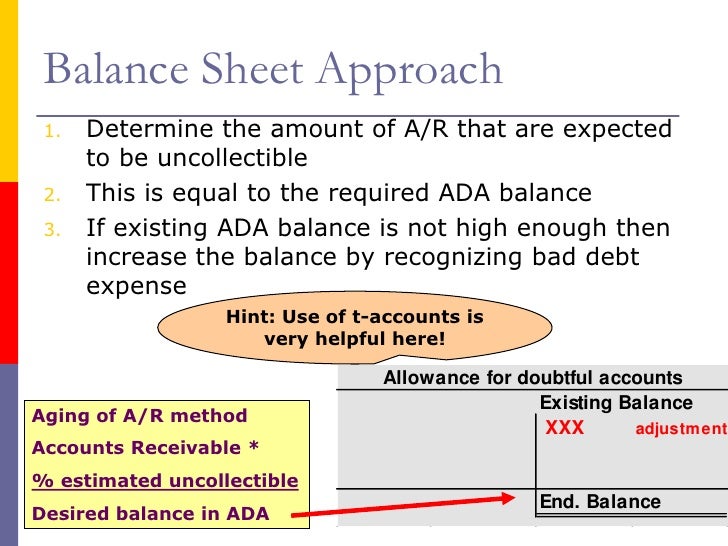
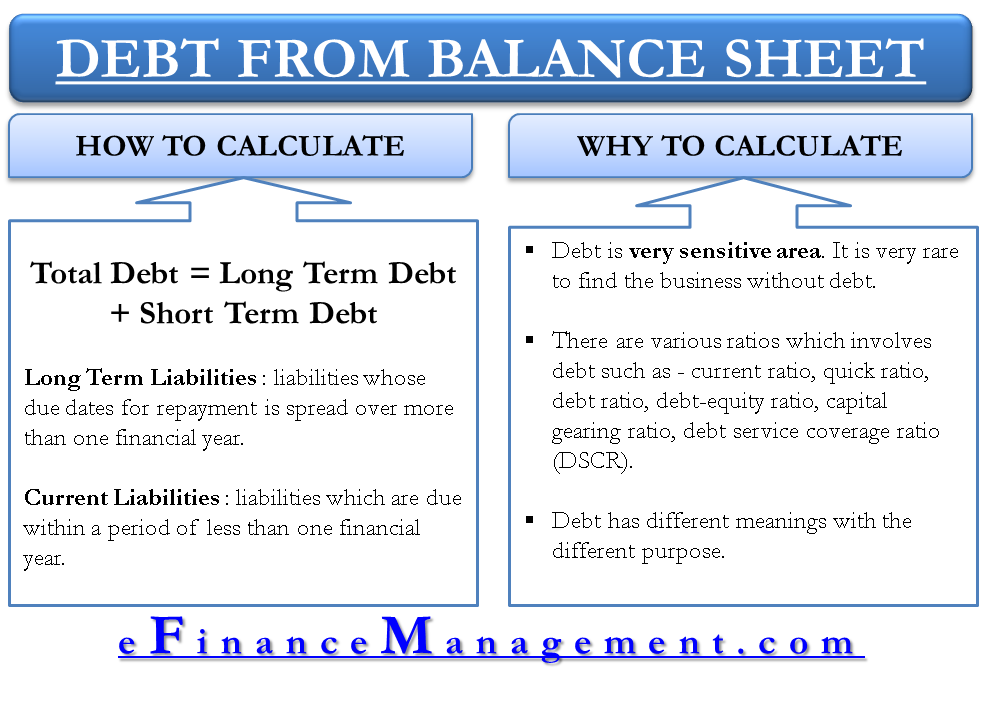
Balance sheet approach bad debt. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. Also called doubtful debts, bad debt expenses are recorded as a negative transaction on your business’s financial statements. Bad debt expense (the figure estimated) must be raised from its present zero balance to $32,000.
Methods of estimating an allowance for bad debt. If uncollectible accounts are expected to be 8 percent of that amount, the expense is reported as $32,000 ($400,000 × 8 percent). To record bad debts in the account books, firms must initially estimate their potential losses.
The percentage of receivables method is otherwise known as the balance sheet approach. The method looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected. It’s recorded separately to keep the balance sheet clean and organized.
There are two main ways to estimate an allowance for bad debts: The method looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected. Before computing the bad debts estimate, you must first determine the balance of a/r at the end of the period then multiply it with the estimated uncollectibility rate.
The difference between the current balance of allowance for doubtful accounts and the amount calculated using the balance sheet approach is the amount of bad debt expense for the period. Using the same information as before, rankin makes an estimate of uncollectible accounts at the end of the year. Bad debts expense is based on a percentage of ending receivables.
On the income statement, the bad debt expense is recorded in the current period to abide by the matching principle, while the accounts receivable line item on the balance sheet is reduced by the allowance for doubtful accounts. There are two primary ways to calculate the allowance for bad debt. We will discuss the journal entries and calculations related to bad debt expense when using the balance sheet approach.
The method looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected. The amount of bad debt expense can be estimated using the accounts receivable aging method or the percentage sales method. The allowance method creates a contra asset allowance.
Estimate and record bad debts when the percentage of receivables method is applied. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. There are two ways to do this method:
The percentage of receivables approach (also known as the balance sheet approach) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable.
Every business has its own process for classifying outstanding accounts as bad debts. This approach looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected. The percentage of receivables method is a balance sheet approach, in which the company estimate how much percentage of receivables will be bad debt and uncollectible.


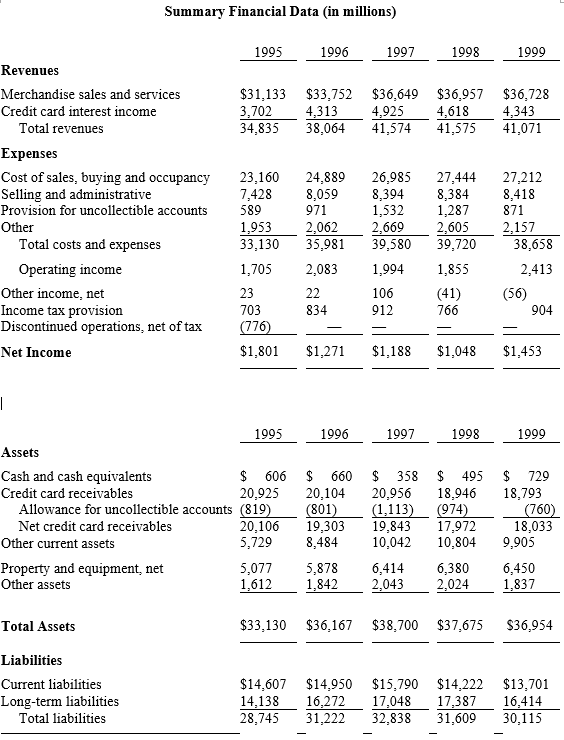
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/AmazonBS-33b2e9c06fff4e63983e63ae9243141c.JPG)




![Making Sense of Your Balance Sheet [Infographic] Learn accounting](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/f7/0d/ec/f70dec3a63cbcc1511efabd76241ea3c.jpg)