Casual Info About Retained Earnings Balance
This accounting formula takes the retained earnings from the previous period, plus the.
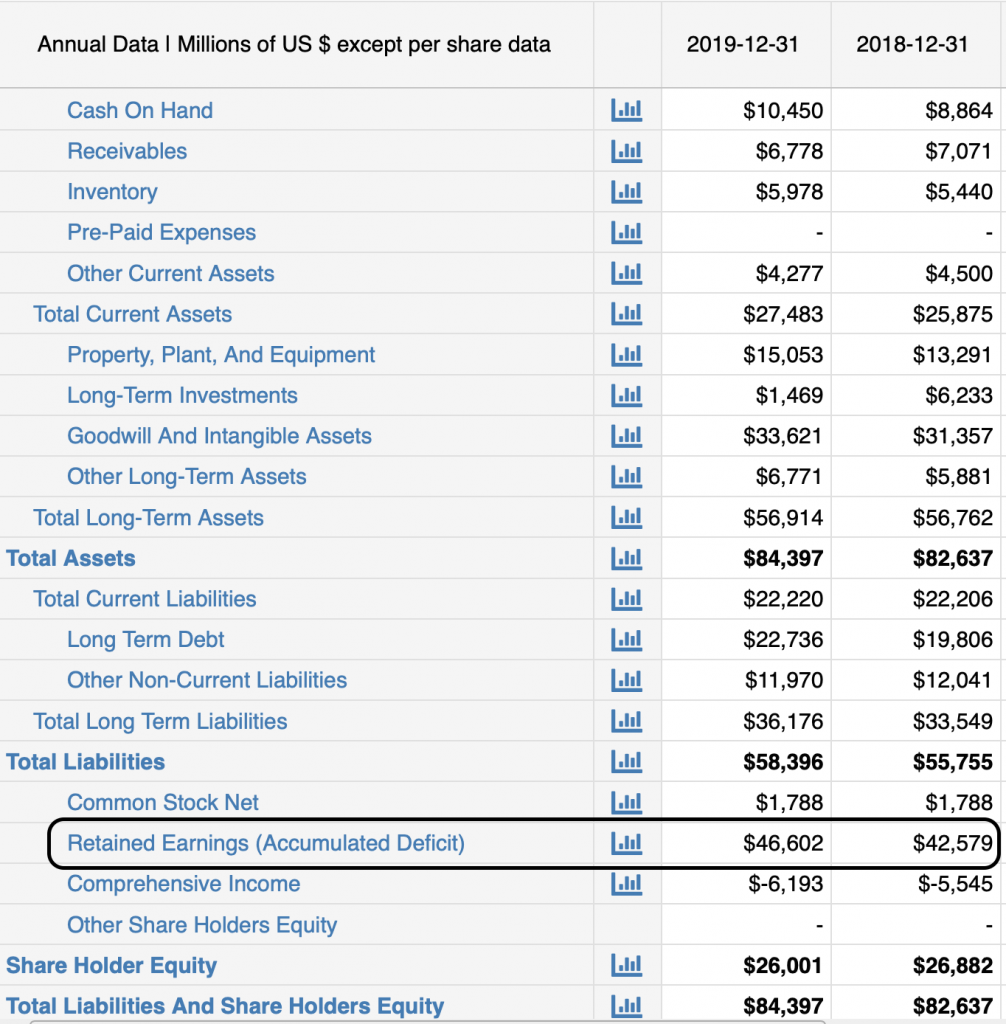
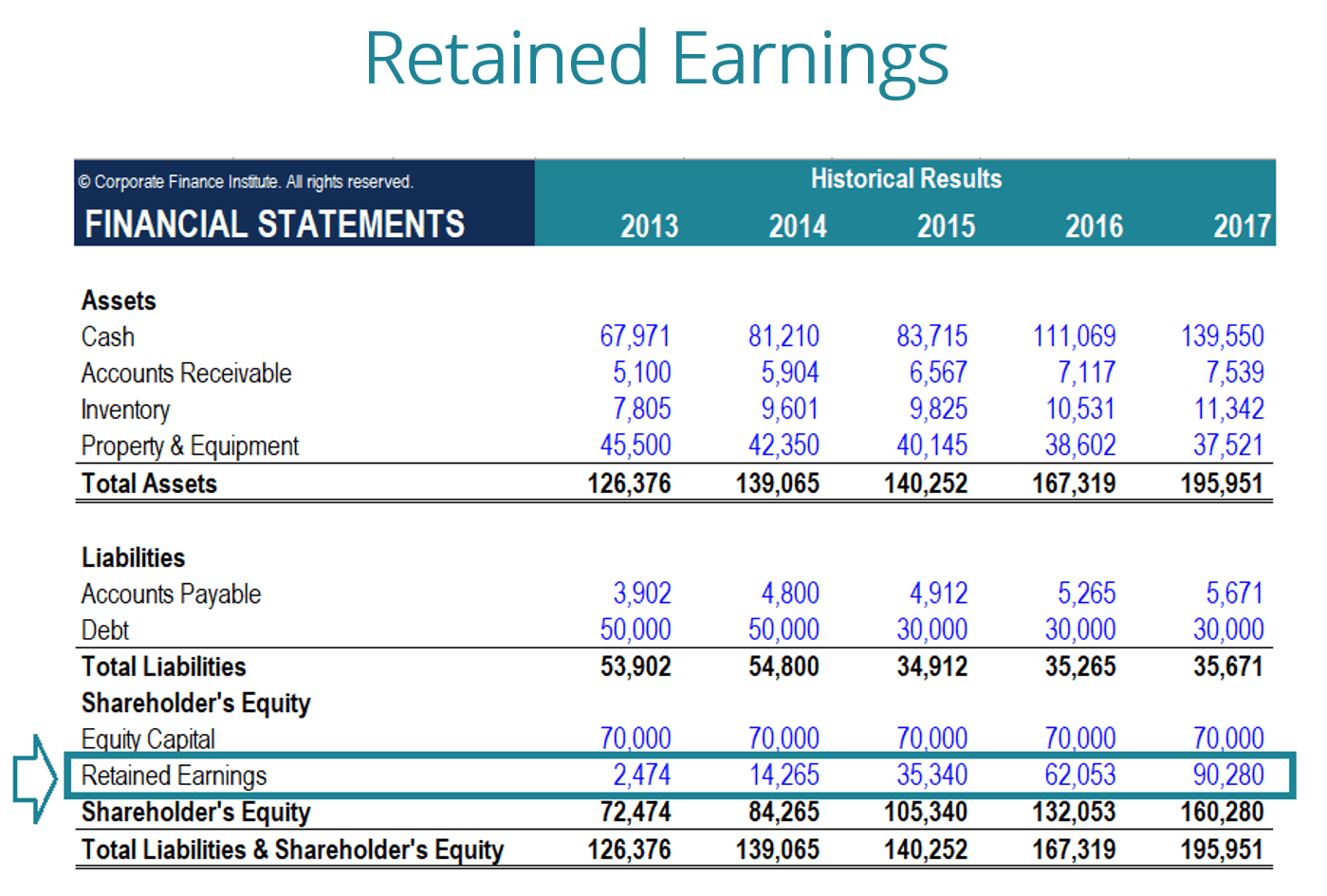
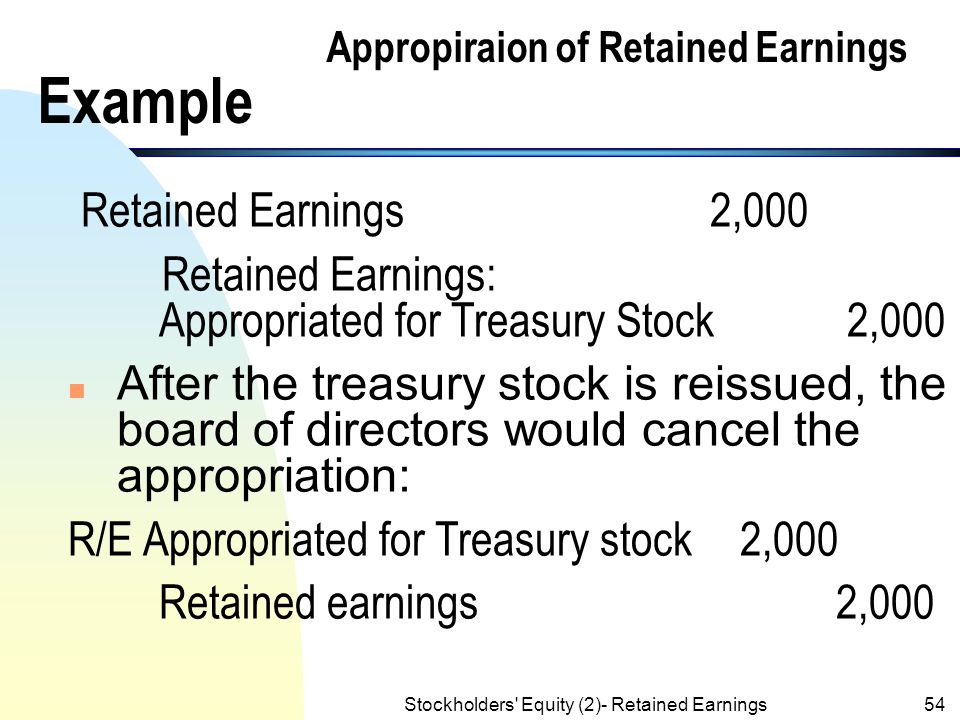
Retained earnings balance. Typically, retained earnings are judged based on their relationship to a company’s total assets. Retained earnings are a portion of every year’s net profit retained after payment of tax and dividend payout. The increase in retained earnings can be found by subtracting the $40,000 in dividend payments from the $100,000 in net.
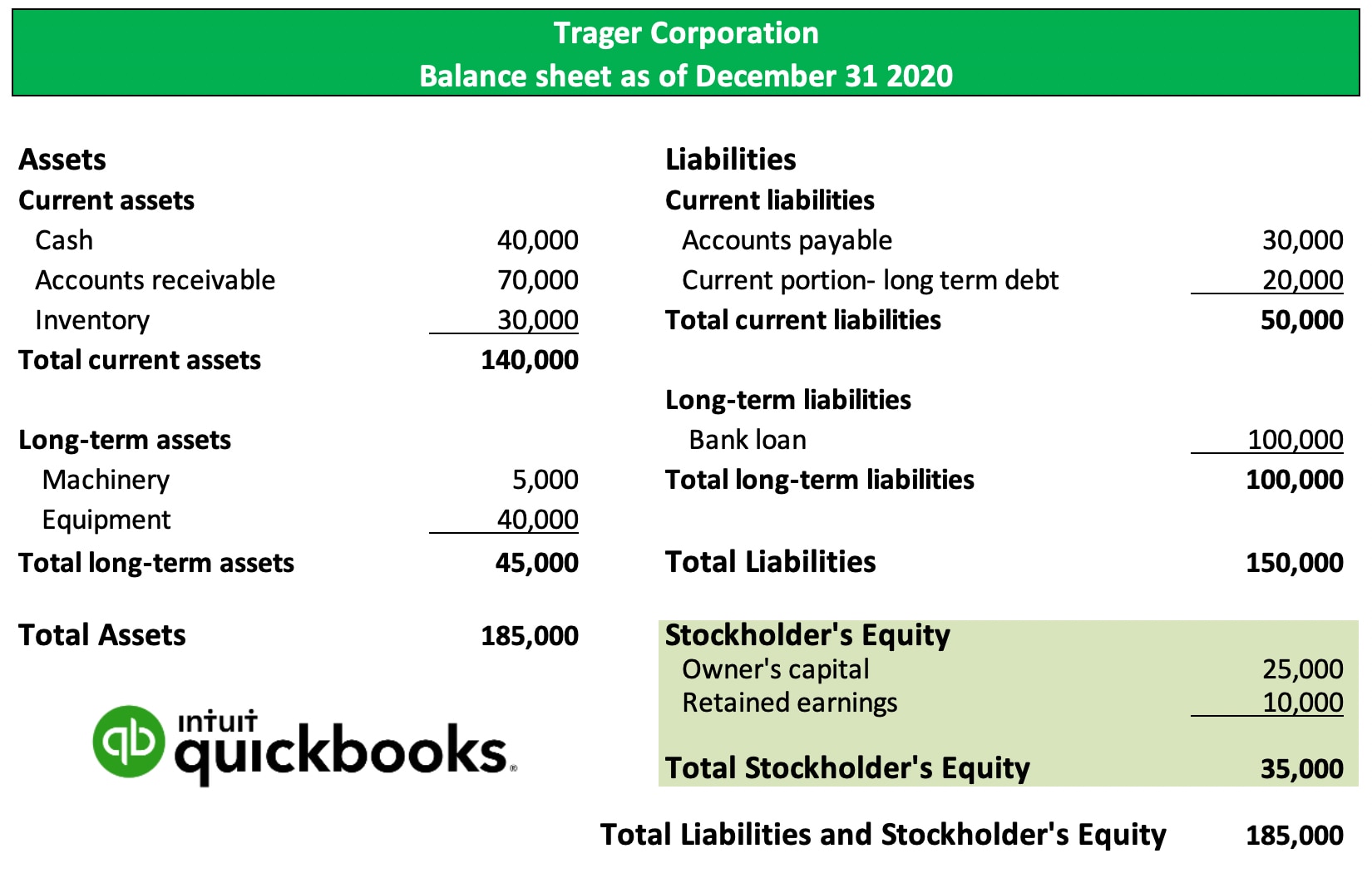
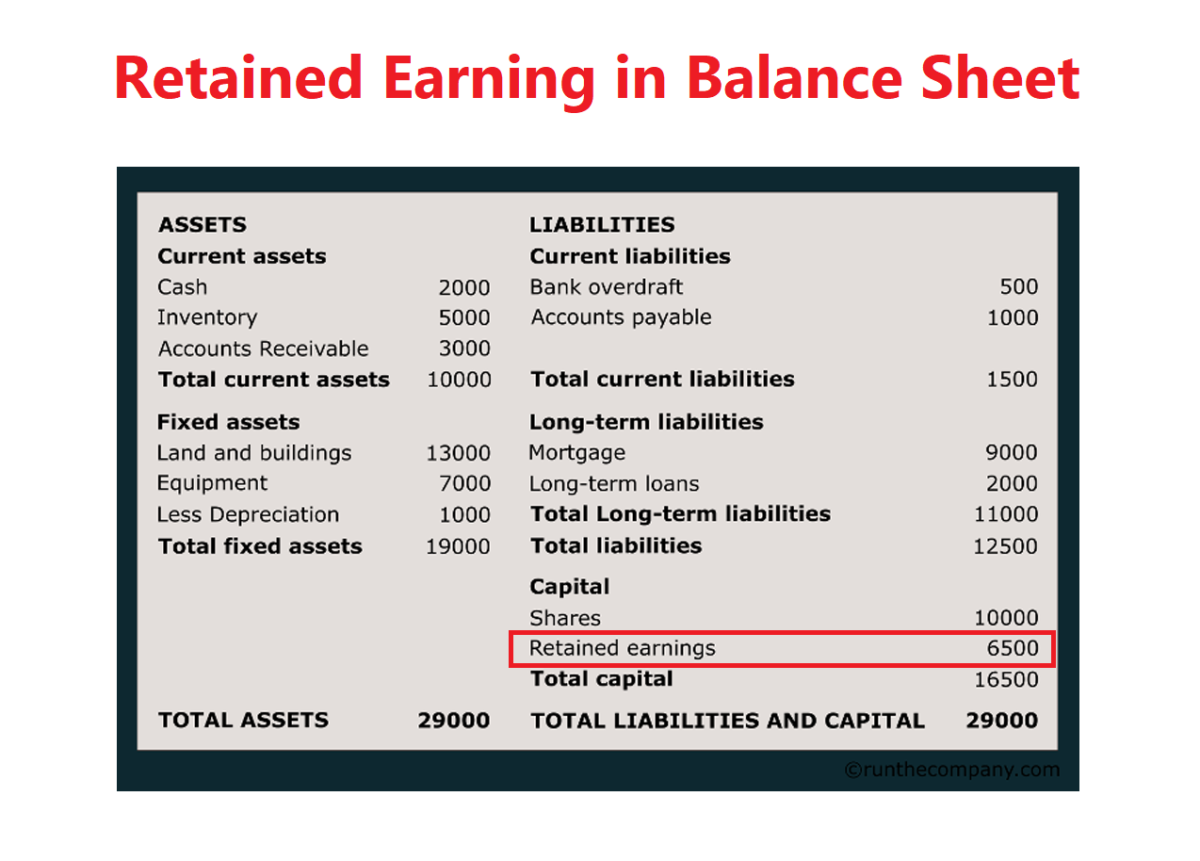
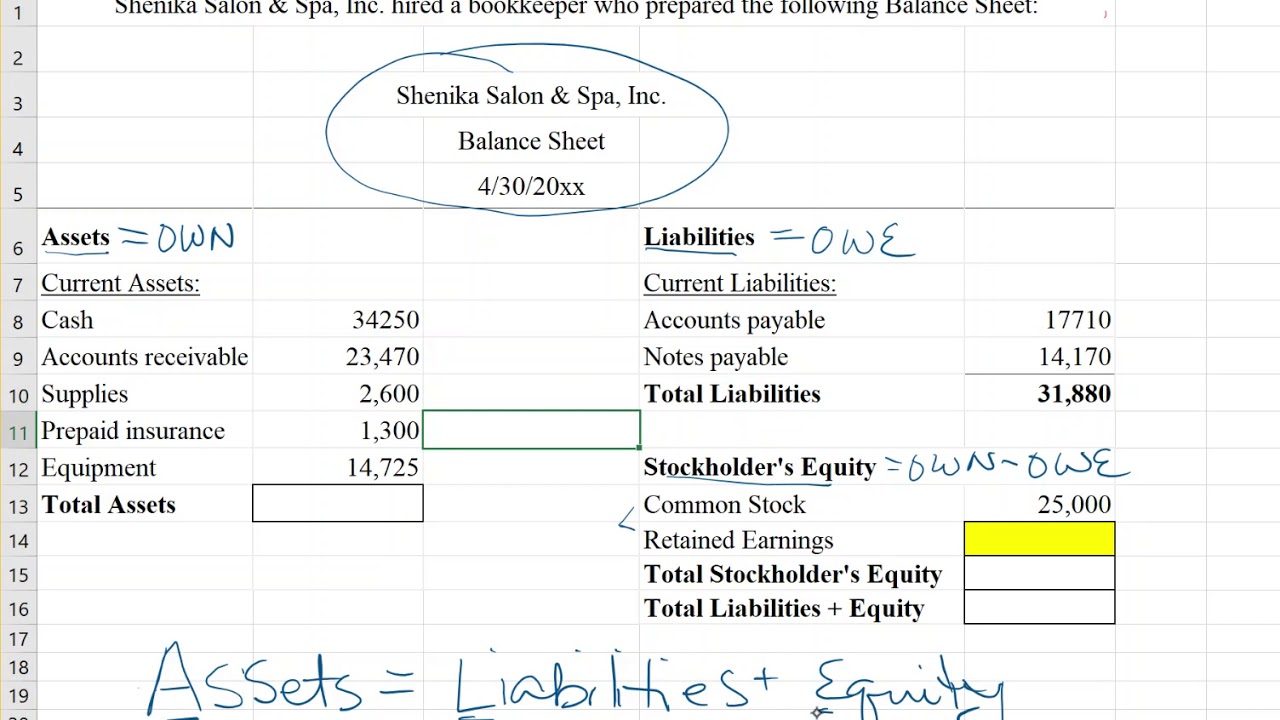
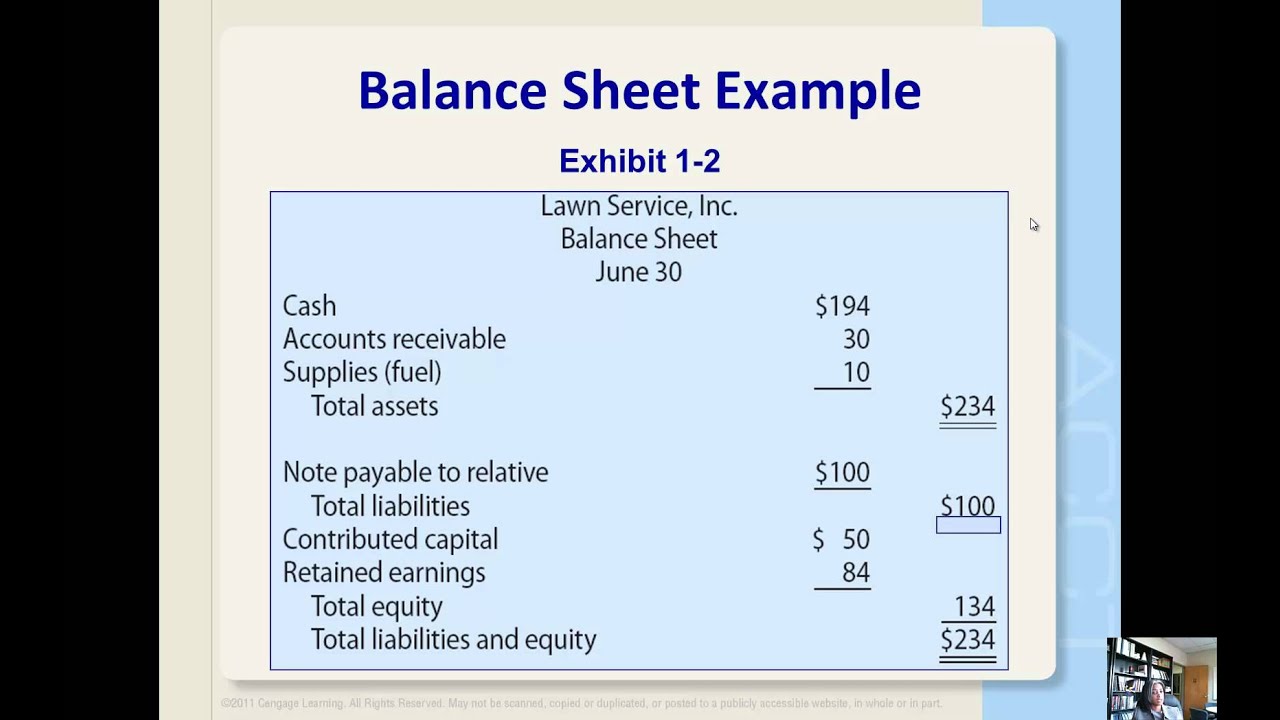
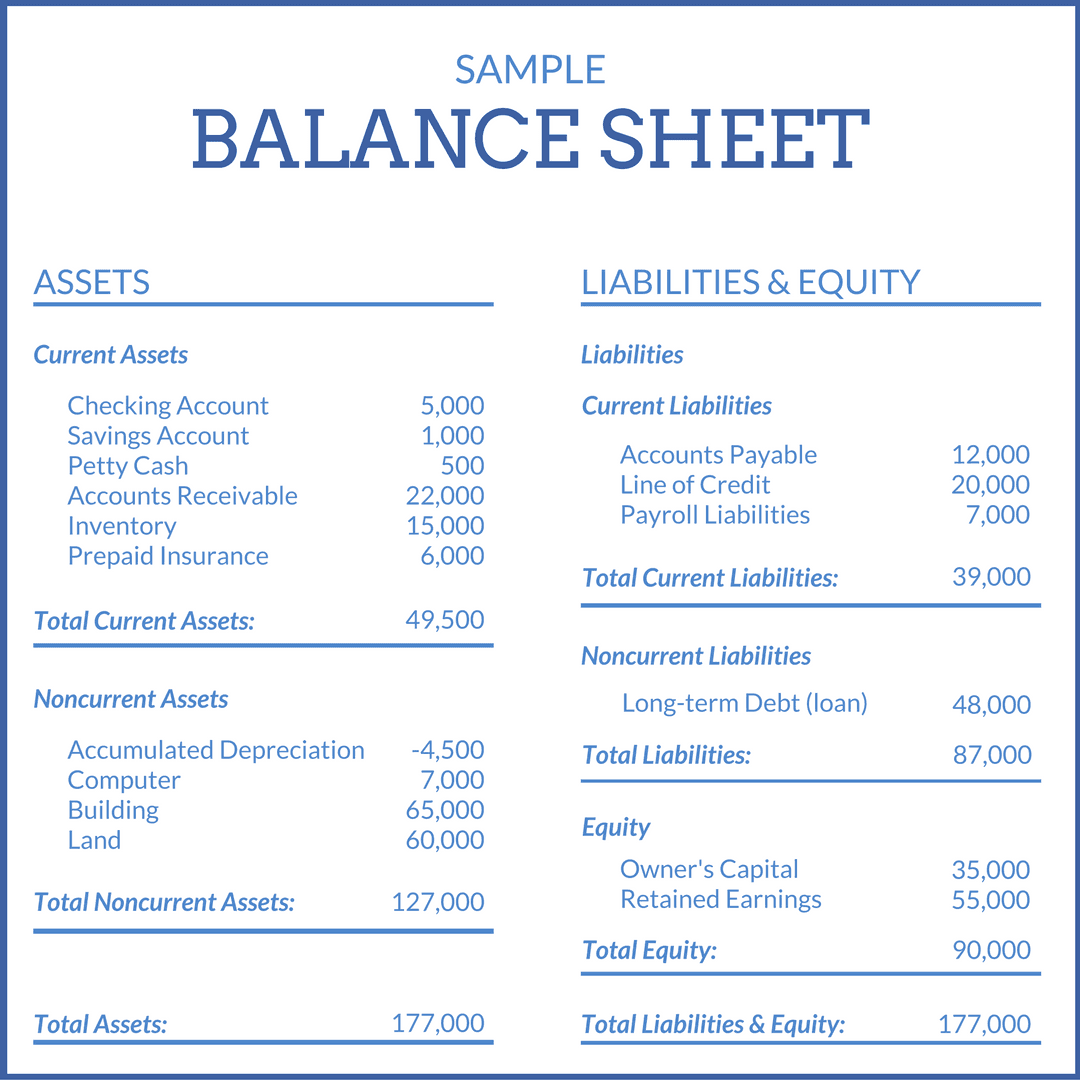
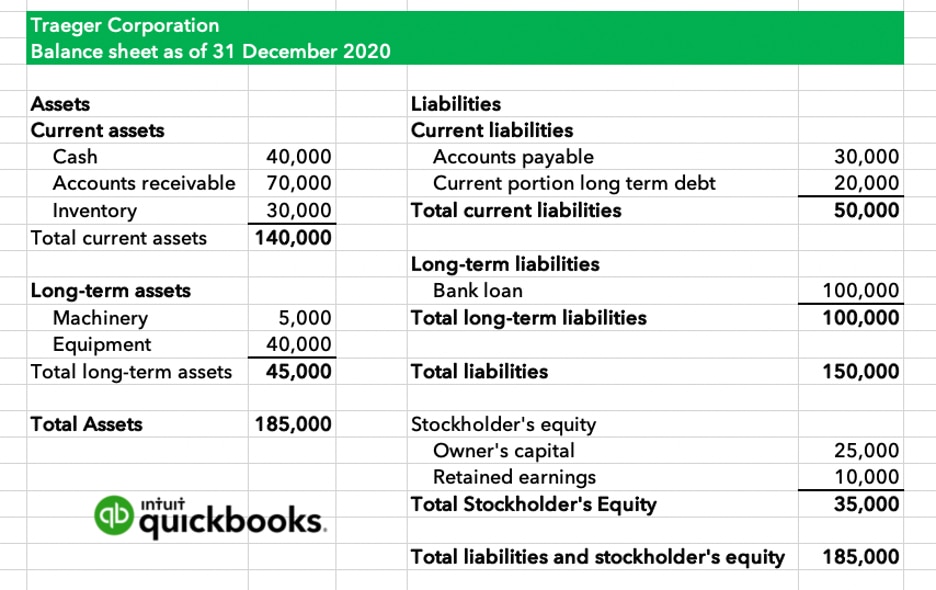
Retained earnings are reported in the shareholders' equity section of a balance sheet. Retained earnings are considered an important concept concerning a. This represents a retention ratio of 0.4.
Retained earnings appear on the balance sheet under the shareholders’ equity section. They can be reported on the balance sheet and earnings statement. However, they are calculated by adding the current year’s net.
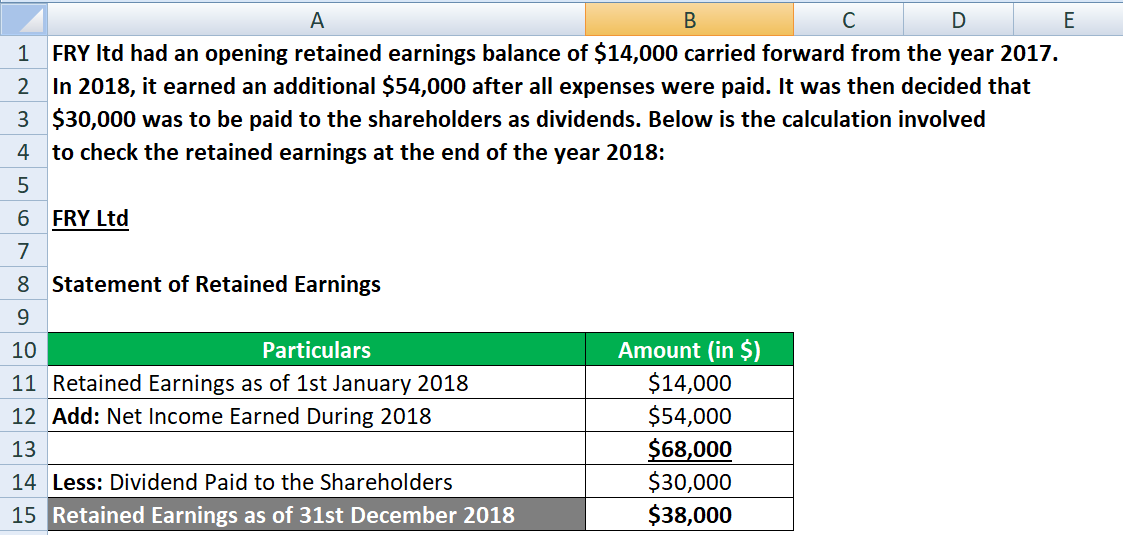
The retained earnings formula is simple. Retained earnings (re) are calculated by taking the beginning balance of re and adding net income (or loss) and then subtracting out any dividends paid. Retained earnings are an accumulation of a company's net income and net losses over all the years the business has been operating.
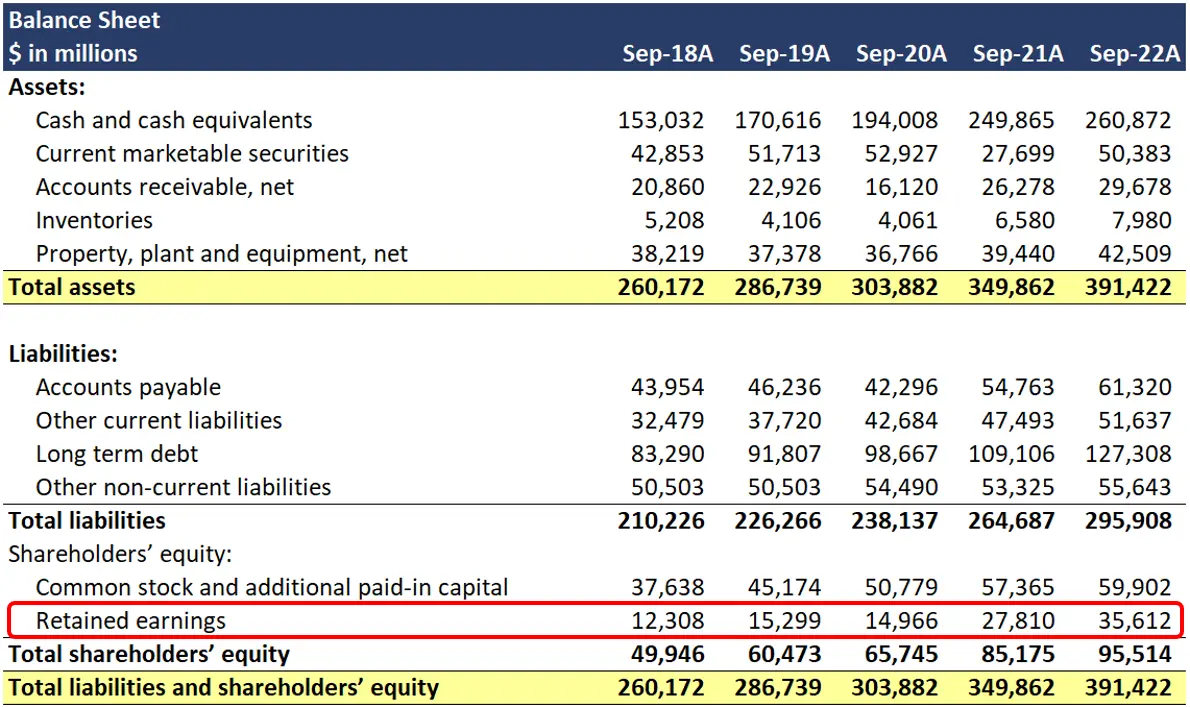
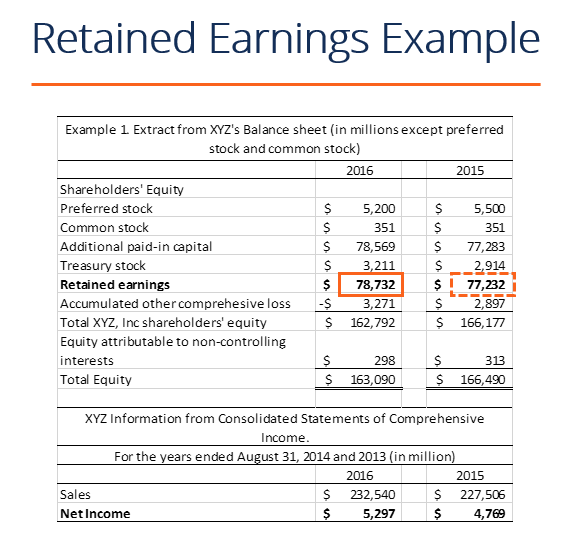
Retained earnings on a balance sheet are the amount of net income remaining after a company pays out dividends to its shareholders. Retained earnings on a balance sheet are those profits that a company. Retained earnings capture the cumulative profits or net earnings a company has produced over a period of time after accounting for any dividends paid to shareholders.
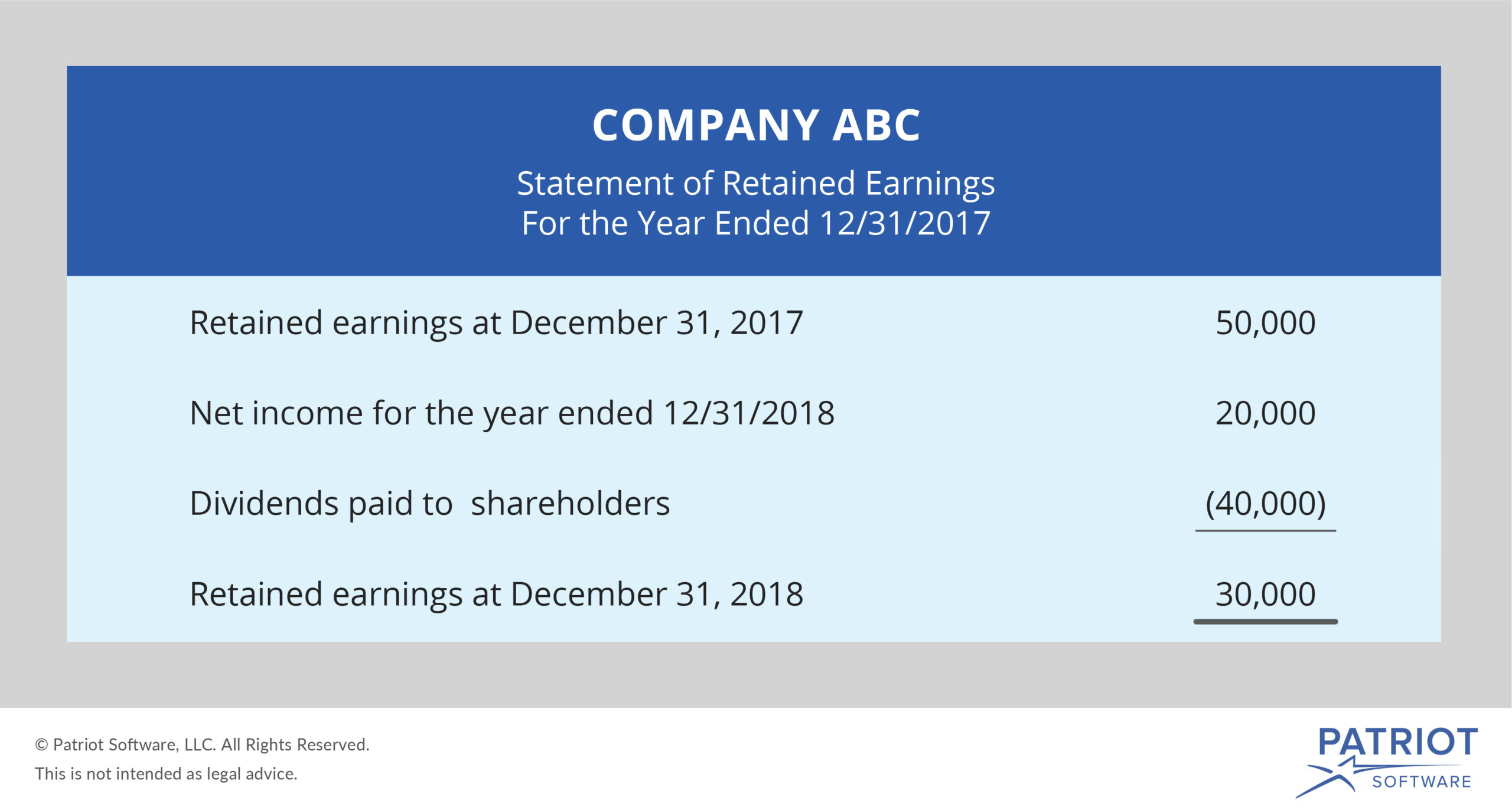
Retained earnings and dividends represent different paths for a company’s net income. Retained earnings are also known as accumulated earnings, earned. Retained earnings are the cumulative net earnings (profit) of a company after paying dividends;
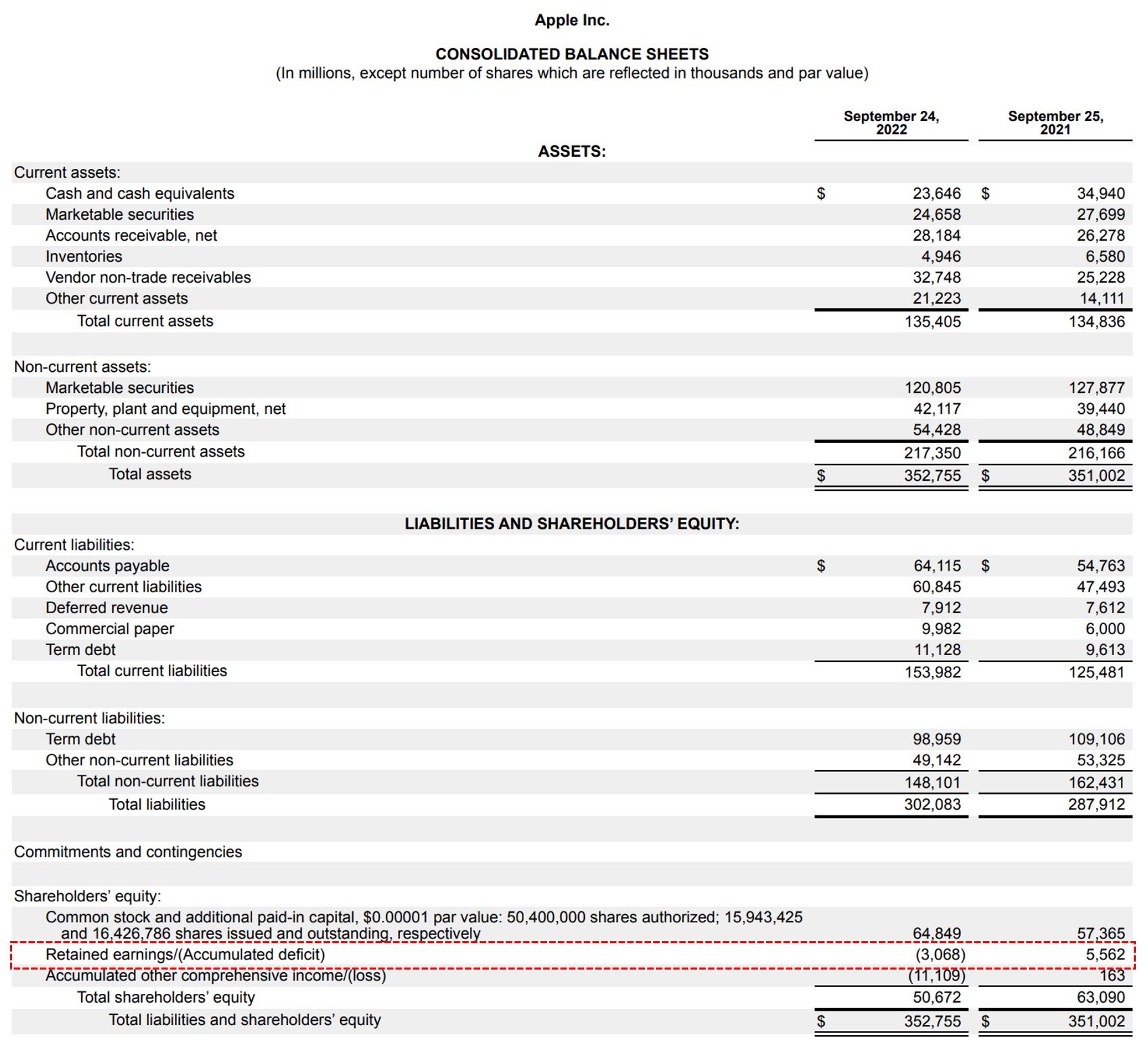
In the next accounting cycle, the re ending balance from the previous accounting period will now. At the end of each accounting period, retained earnings are reported on the balance sheet as the accumulated income from the prior year (including the current year’s income), minus dividends paid to shareholders.