Simple Info About Interest Coverage Ratio Interpretation

For the full year, the.
Interest coverage ratio interpretation. The interest coverage ratio depicts the number of times a company can pay its interest expenses within a financial year or quarter using its current earnings. The interest coverage ratio is a financial ratio to measure a company’s ability to pay interest expense using the profit it generates. Interpretation of interest coverage ratio.
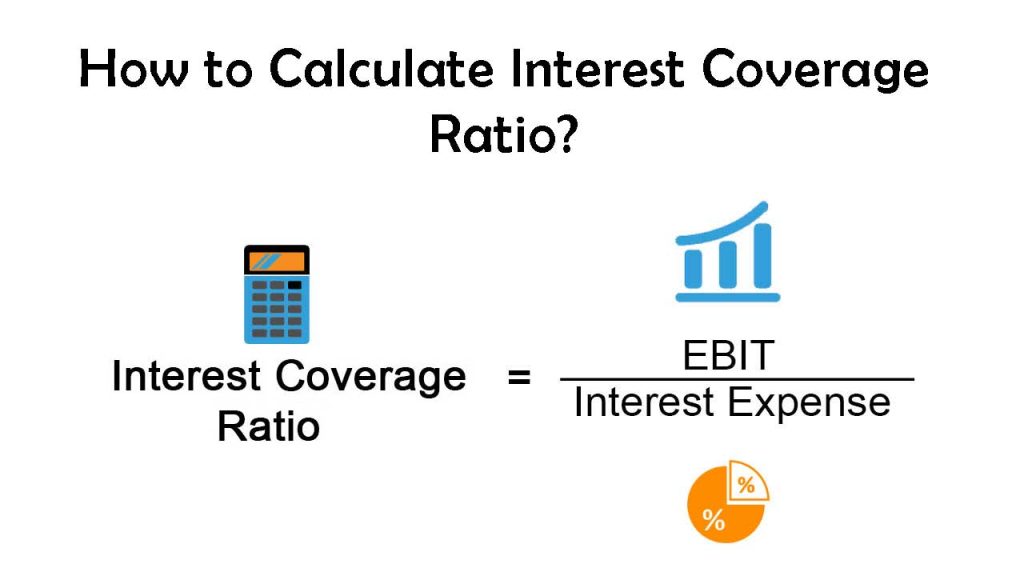
The interest coverage ratio can be represented by the following formula. The company may struggle to meet interest payments and could risk default. It helps them understand whether the companies borrowing the money would be able to manage interest payments for multiple borrowings at a.
If the ratio is low, it. The interest coverage ratio is a debt and profitability ratio used to determine how easily a company can pay interest on its outstanding debt. Earnings before interest and tax (ebit) is a commonly used profit metric.
Trump, searingly refuted allegations that she. If the ratio is high, the business has sufficient profits to pay off the interest expense without hurting its finances. The interest coverage ratio (icr), also called the “times interest earned”, evaluates the number of times a company is able to pay the interest expenses on its debt with its operating income.
With everything on the line, fani willis delivered raw testimony. Interpretation of interest coverage ratio if a company's interest coverage ratio (icr) is high, it shows that interest payments are not a major part of the company's total expenses. It proposed a dividend of 0.10 crowns per a and b share, down from 0.40 crowns last year.
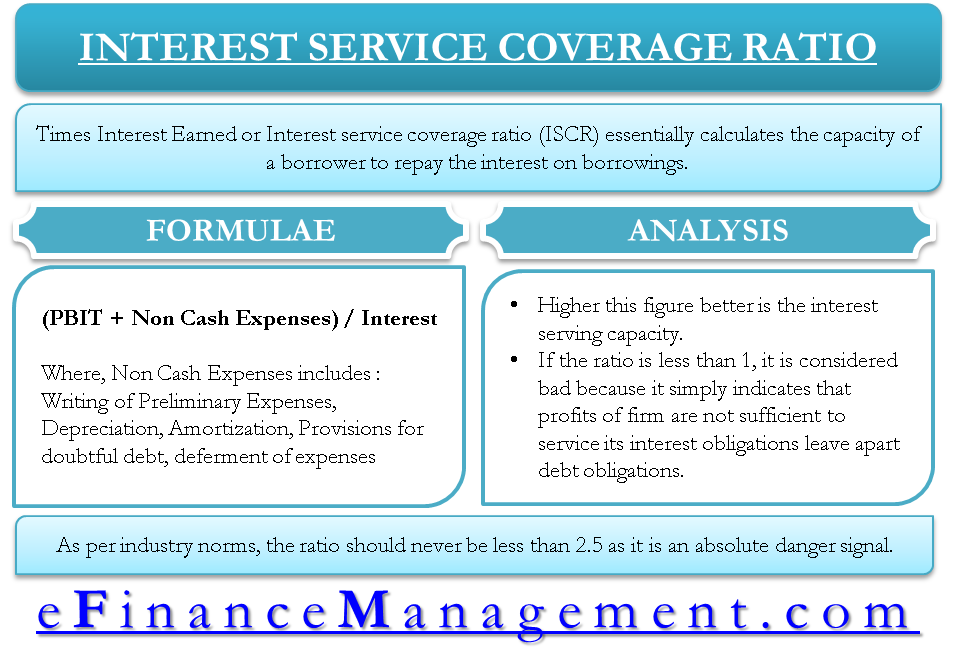
Additionally, a ratio of 1.5 might be thought to be adequate. Unlike the debt service coverage ratio , this liquidity ratio really has nothing to do with being. Willis, the district attorney overseeing the georgia prosecution of donald j.
4 types of interest coverage ratio 5 importance of the interest coverage ratio 6 factors to note before using interest coverage ratio 7 conclusion 8 faqs 9 related articles Corem's interest coverage ratio, which reflects a company's ability to pay the interest on its outstanding debt, fell to 1.7 in the fourth quarter from 2.0 a year earlier. As a general benchmark, an interest coverage ratio of 1.5 is considered the minimum acceptable ratio.
The interest coverage ratio (often abbreviated as icr) is one of the many solvency checks used by a company to determine its default risk. The company is struggling to meet its interest obligations and may be at risk of defaulting on its loans. Interest coverage ratio is a financial metric that helps assess a company's ability to meet its interest payment obligations on its outstanding debt.
Interest coverage ratio is a metric used for determining the number of times a company can pay off its interest obligation with its current earnings before applicable taxes and interests are deducted. The interest coverage ratio, often abbreviated as icr, is a financial indicator that gauges a company’s capacity to pay the interest on its outstanding debt. The company may exhibit a strong financial health and can readily meet interest commitments.
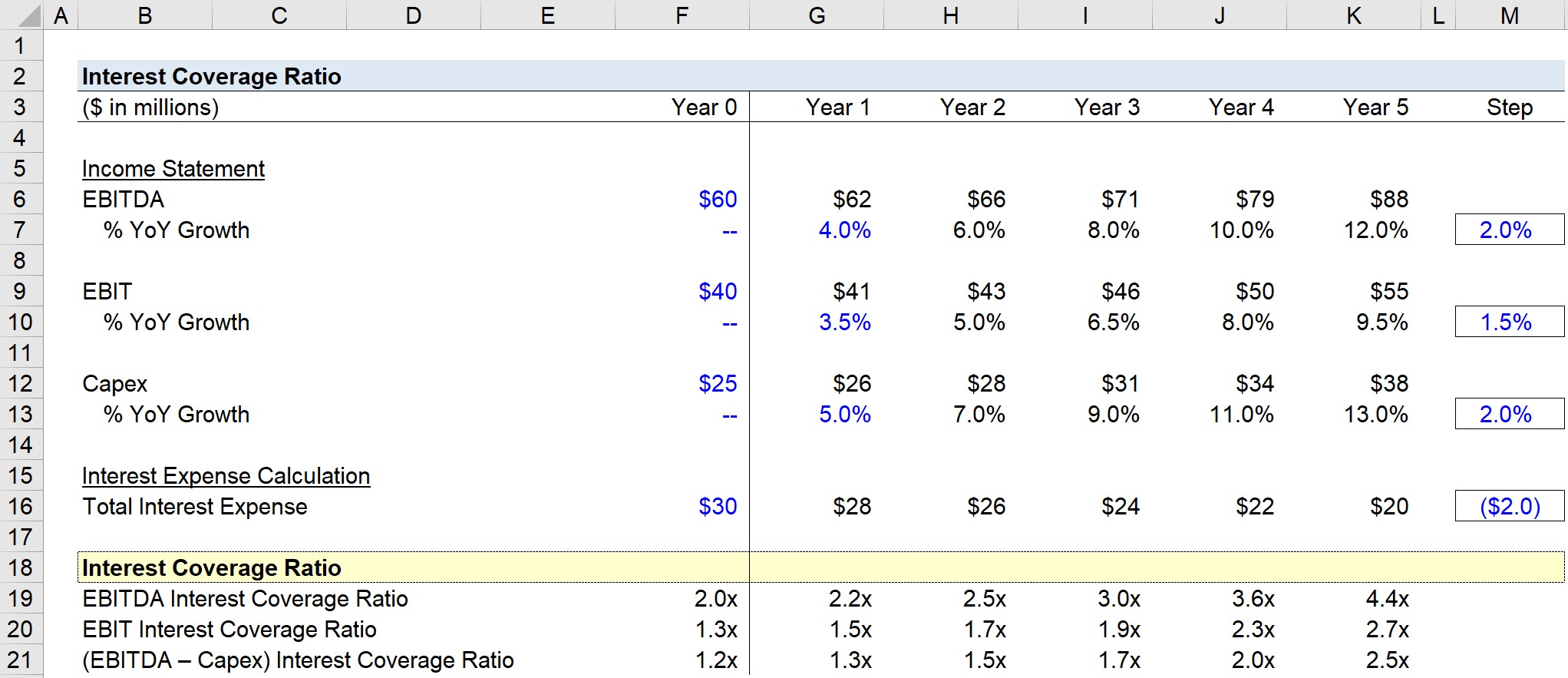
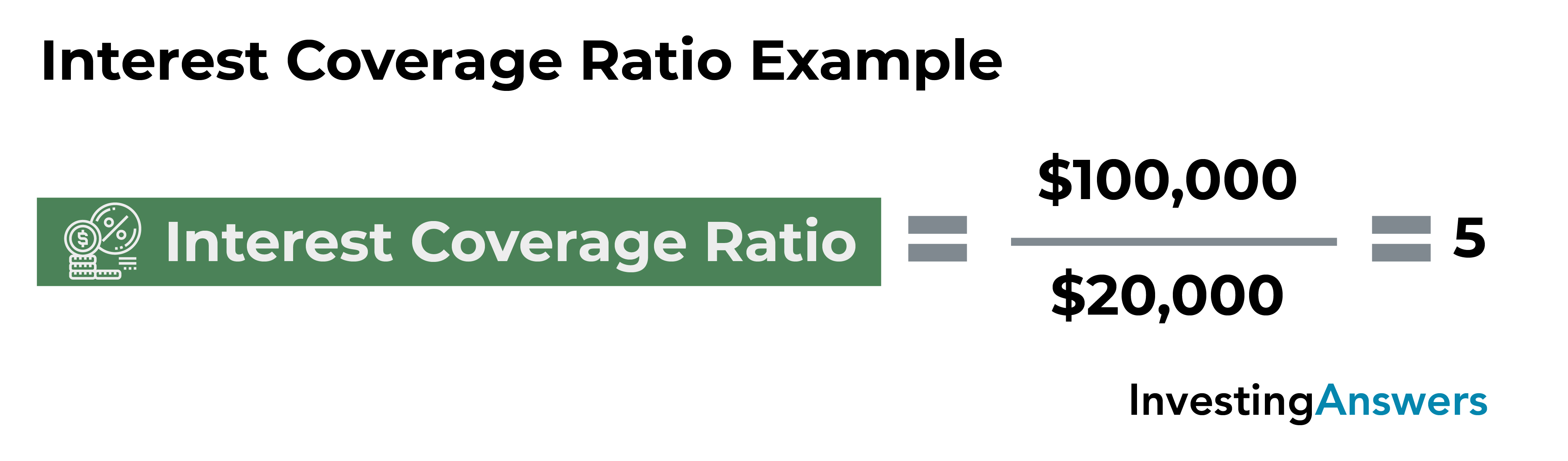
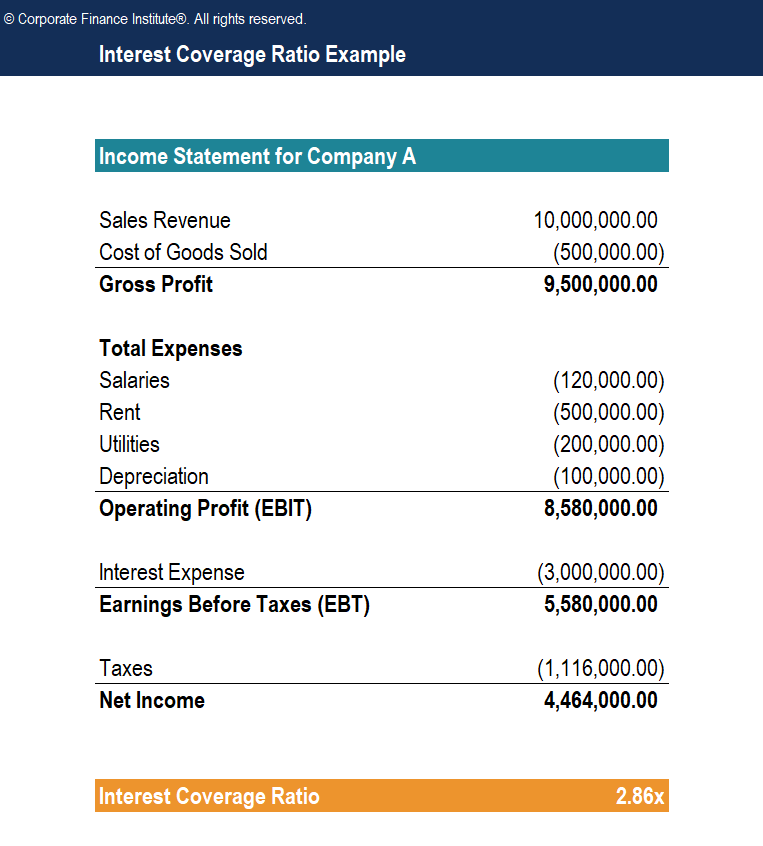
Interest coverage ratio = $8,580,000 / $3,000,000 = 2.86x. The interest coverage ratio is a financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to make interest payments on its debt in a timely manner. To determine the interest coverage ratio:










/GettyImages-1016980902-564d2eee00b64de9b17a1f4c1e76c4ad.jpg)
