Unique Info About Define Retained Earnings On Balance Sheet
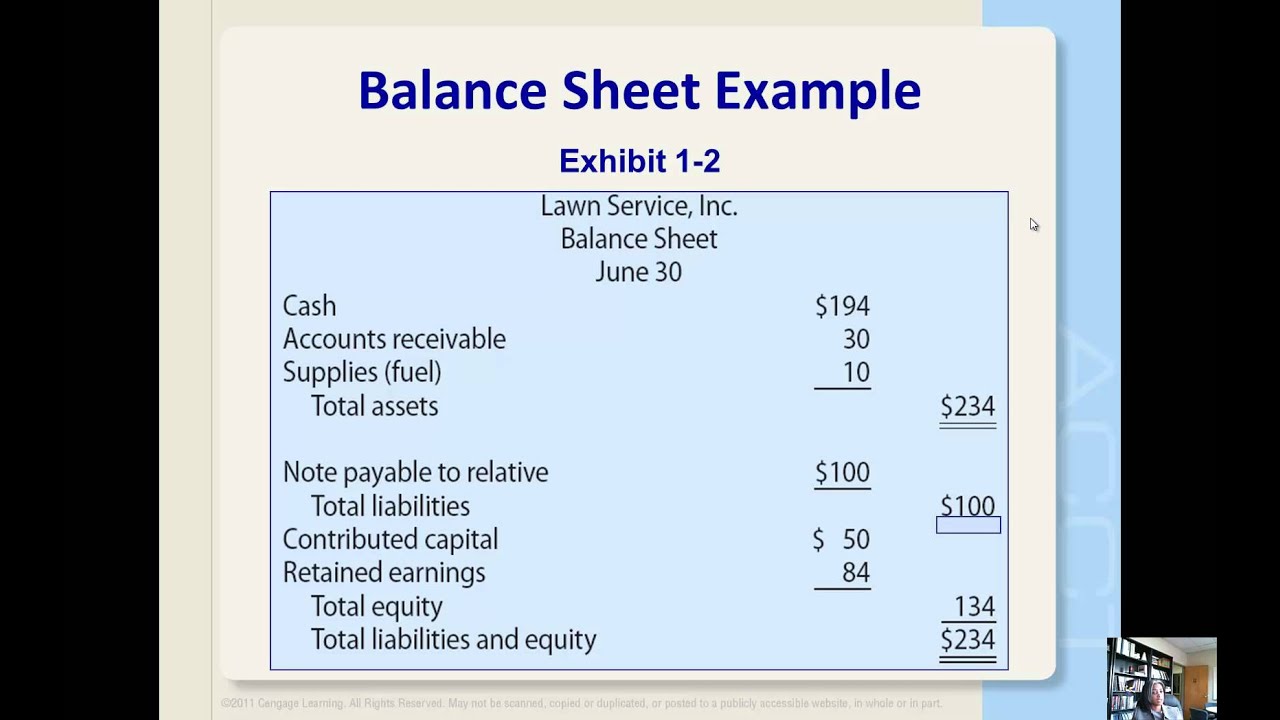
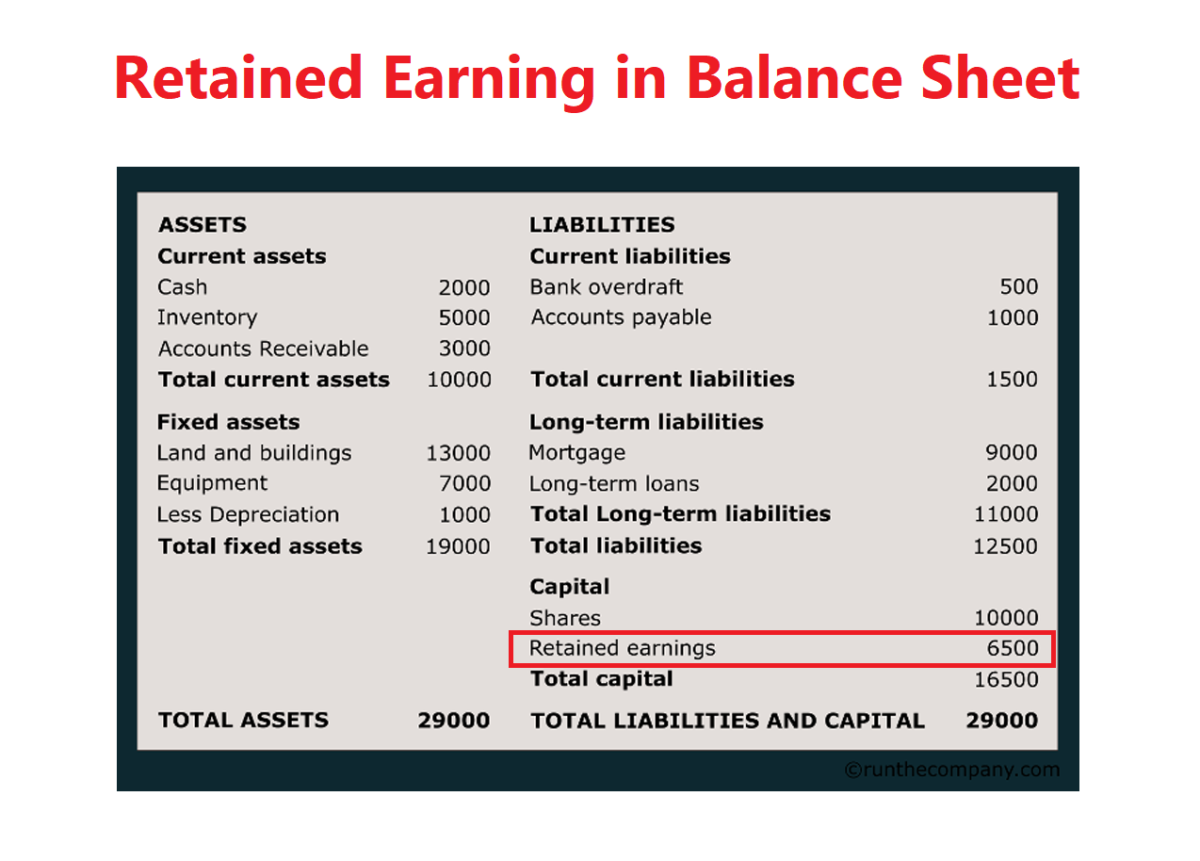
The recording of retained earnings is done on the balance sheet of a company.
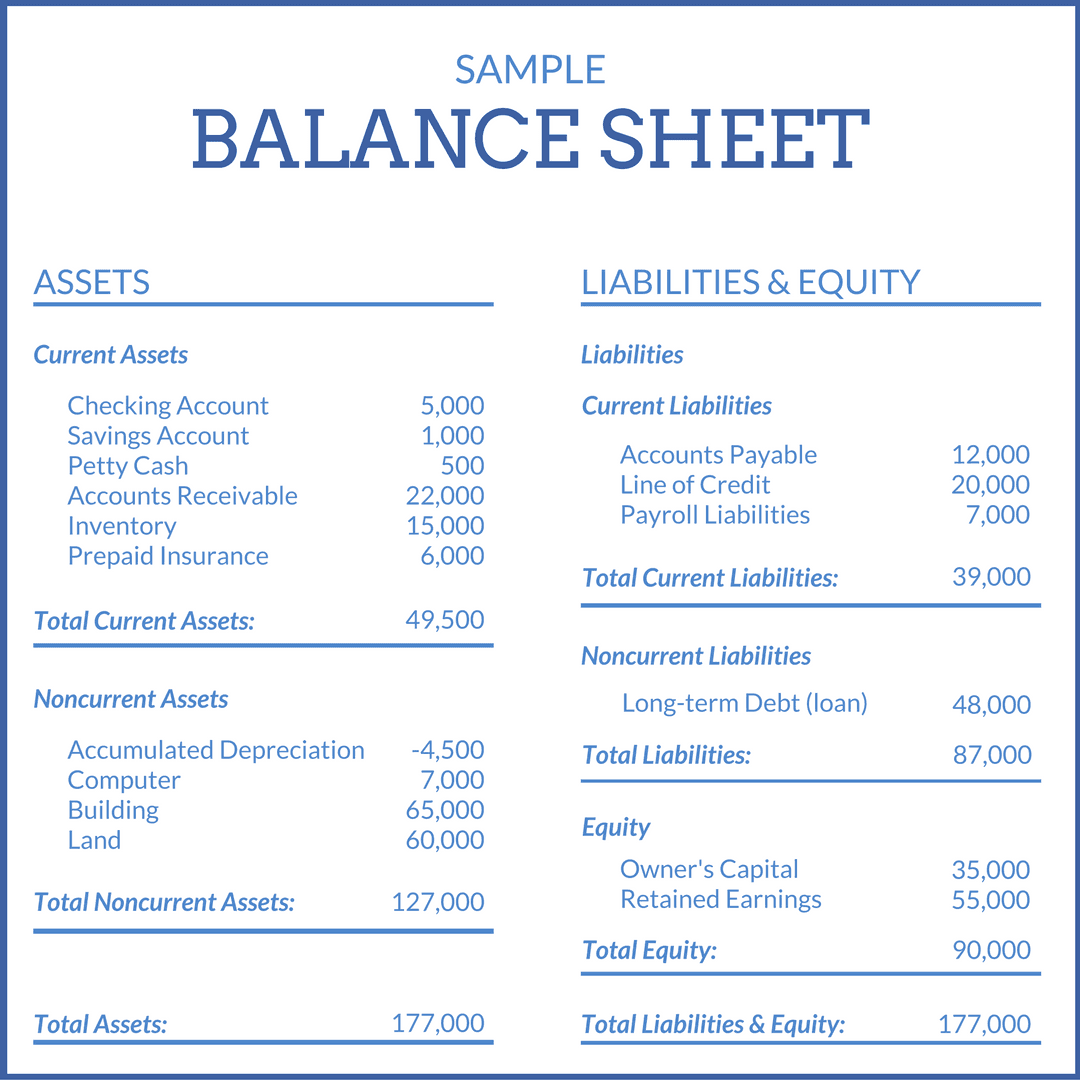
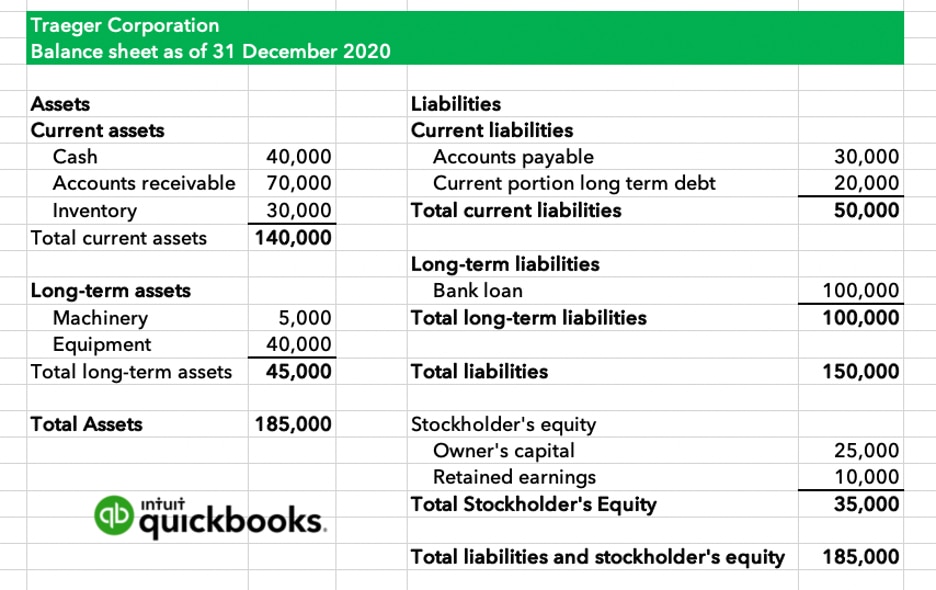
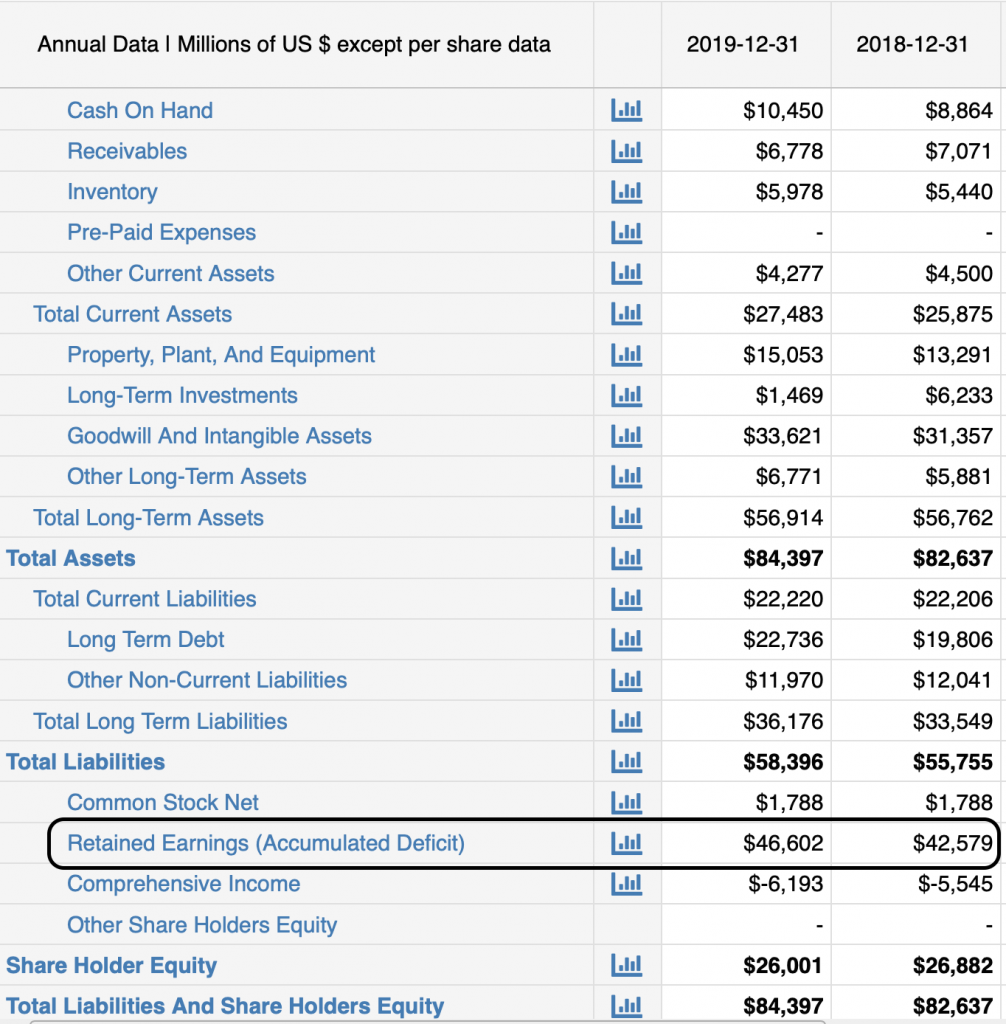
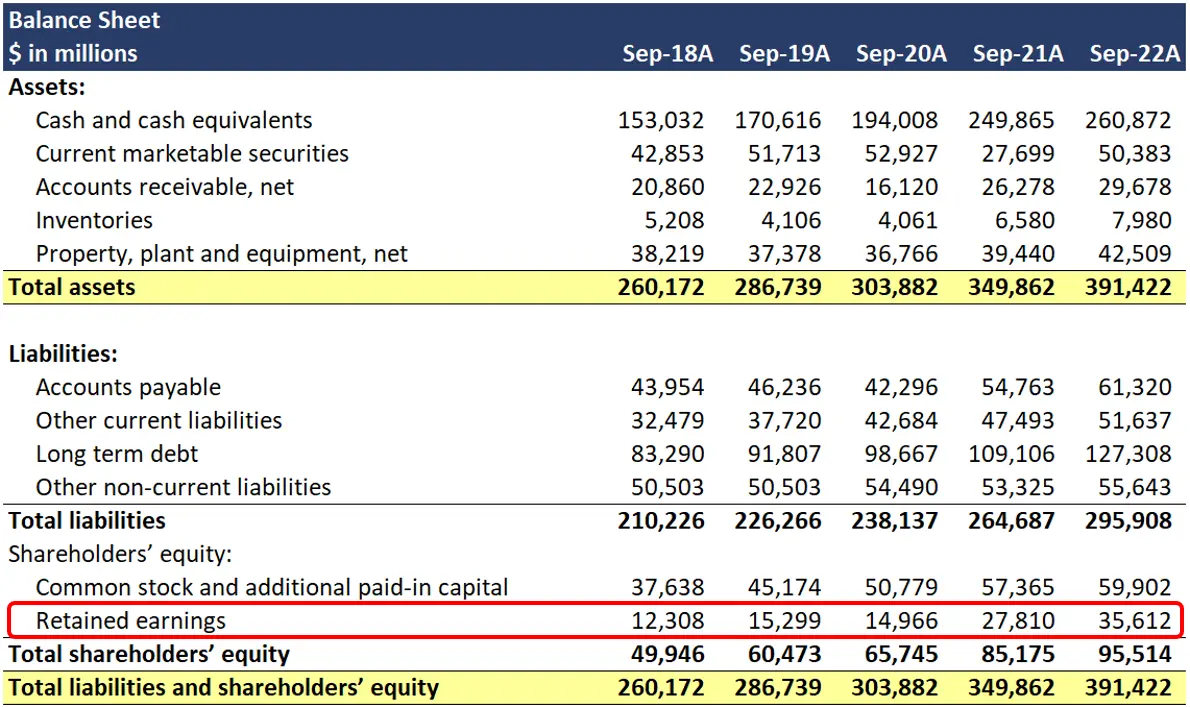
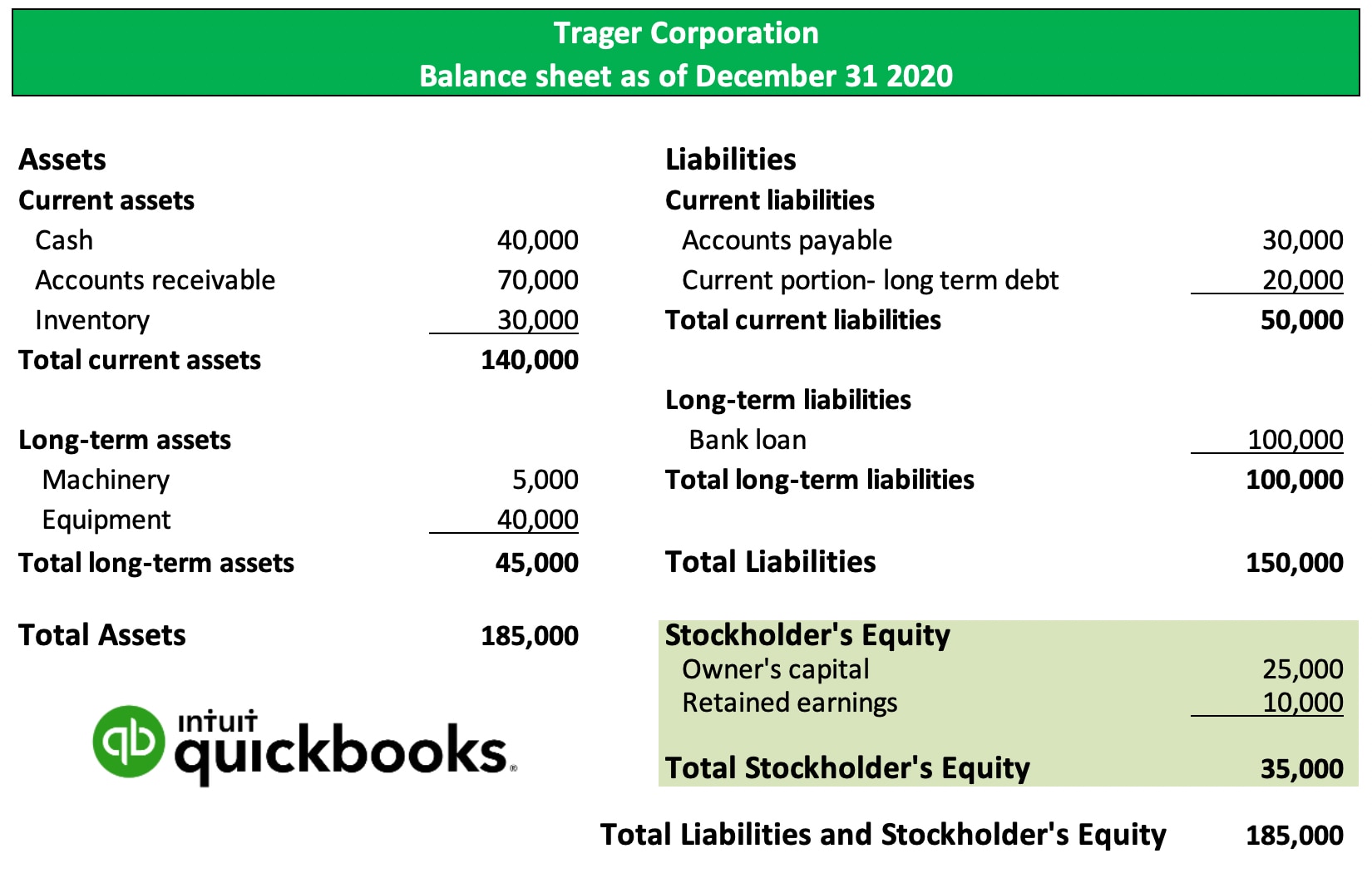
Define retained earnings on balance sheet. Retained earnings refer to a company’s net profit after paying out dividends to shareholders. Retained earnings on a balance sheet are the amount of net income remaining after a company pays out dividends to its shareholders. The retained earnings amount fluctuates as money comes into and goes out of the business.
These retained earnings are often reinvested in the company, such as through research and development, equipment replacement, or. Retained earnings are the amount of profit a company has left over after paying all its direct costs, indirect costs, income taxes and its dividends to shareholders. Sometimes a separate statement for the.
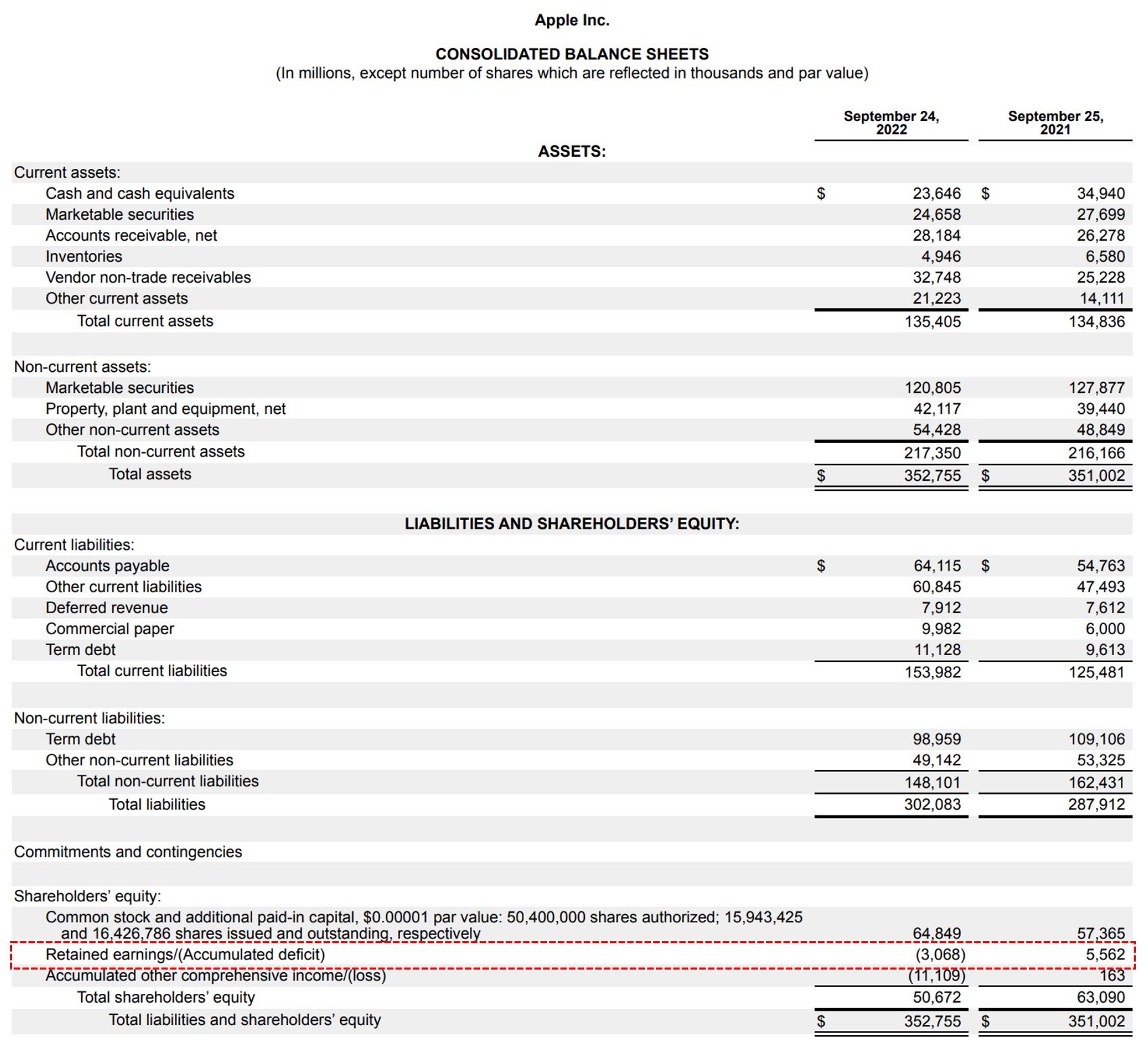
Retained earnings are the lifeblood of a company’s financial growth and sustainability. Retained earnings (re) are the amount of net income left over for the business after it has paid out dividends to its shareholders. The retained earnings figure is not always a positive number.
In human terms, retained earnings are the portion of profits set aside to be reinvested in your business. The retained earnings figure on the balance sheet reflects the company's accumulated net income, after paying out dividends, since the company's inception. The figure from the end of one accounting period is transferred to the start of the next, with the current period’s net income or loss added or subtracted.
Expansion, investment, debt reduction, and stock repurchasing are four common uses of a company’s retained earnings balance. This post will illuminate what retained earnings on a balance sheet are and the steps to calculate them. This amount gives companies clarity on how much money their business has after paying off all their dues, including the share of the investors.
It's a key indicator of the company's ability to generate profits and create value for shareholders over time. Retained earnings on the balance sheet measures the accumulated profits kept by a company to date since inception, rather than issued as dividends. Retained earnings are noted on the balance sheet under accumulated income from the previous year minus shareholder dividends.
Either way, they push up the net worth (or owner’s equity) of the business. The decision to retain the earnings or distribute them among. If liabilities (debts) stay constant, then an increase in assets will drive up owner’s equity.
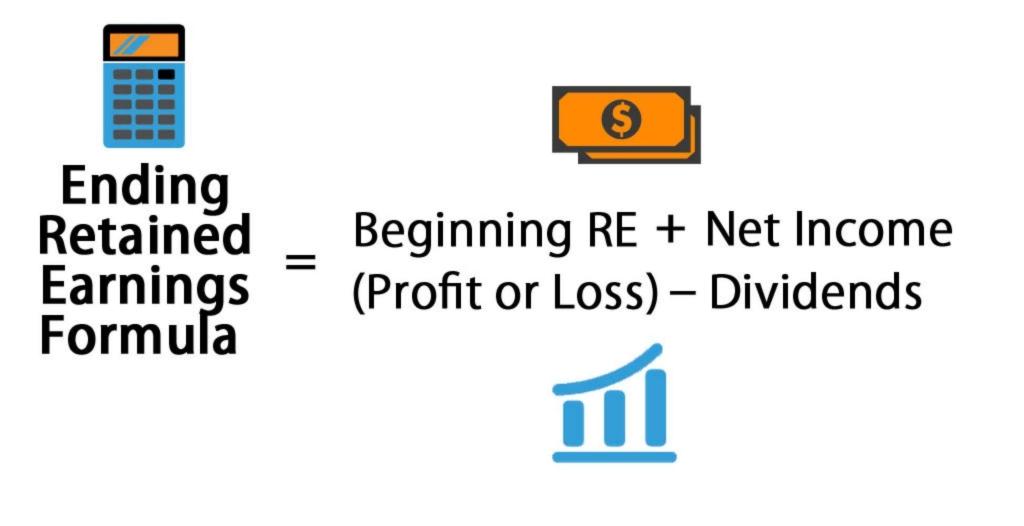
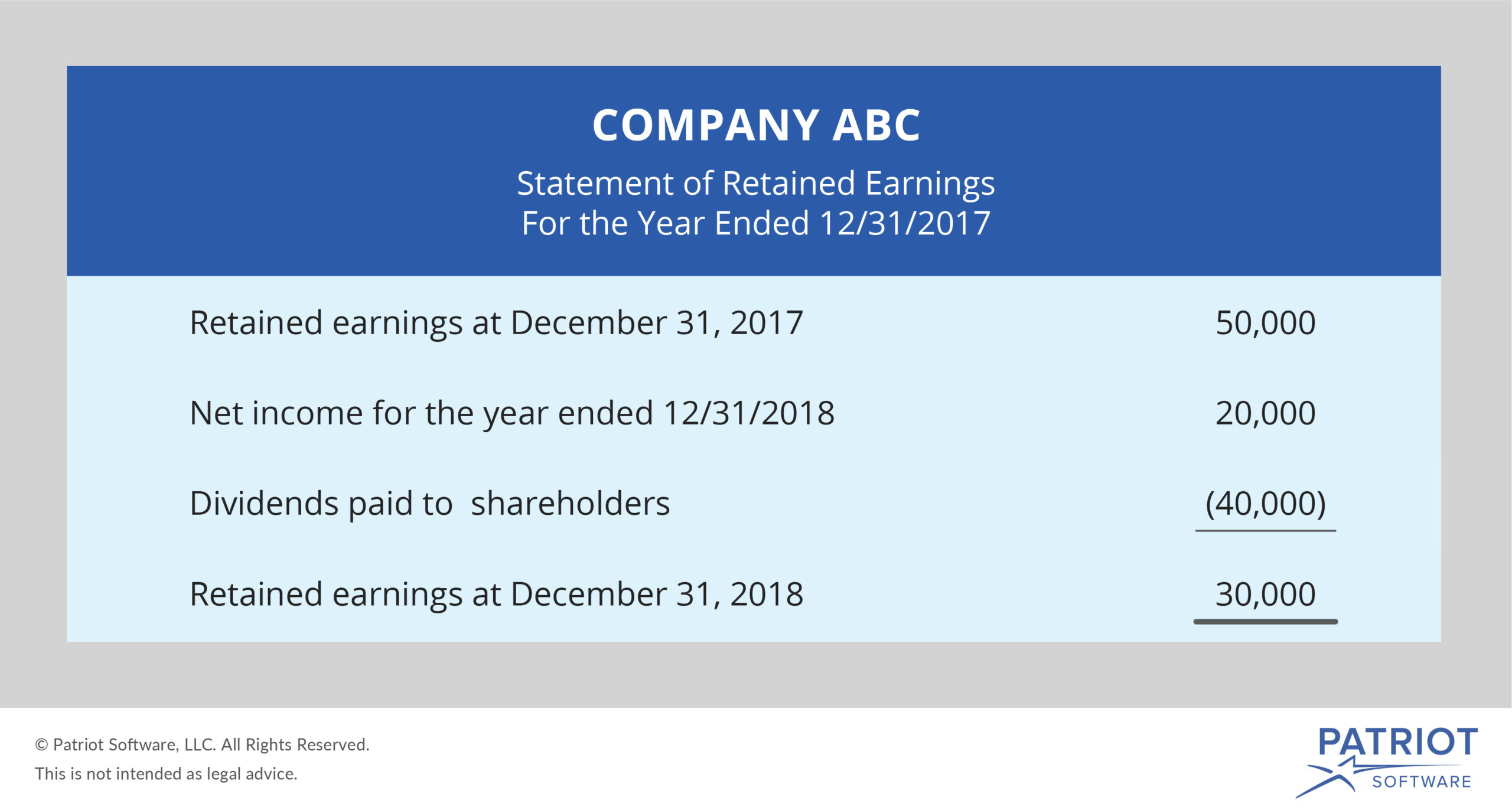
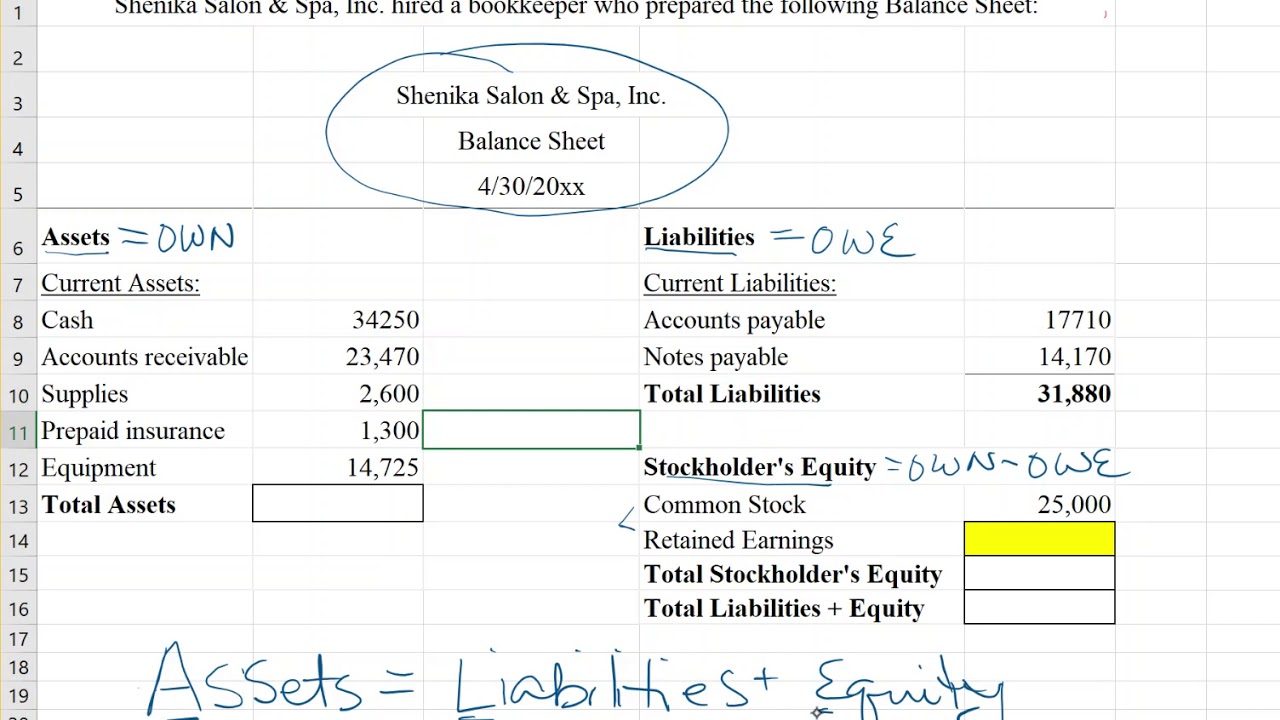
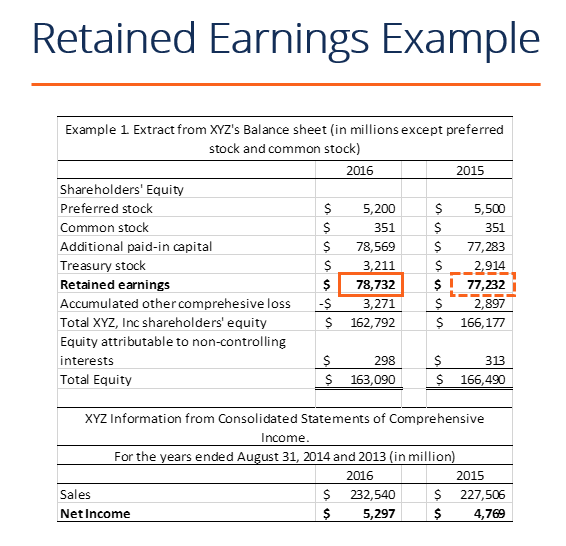
Retained earnings are cumulative on the balance sheet. Essentially, you find your retained earnings by adding together your beginning holdings and your net income or loss for the accounting period, and then you subtract all dividends paid out (both cash and stock). Retained earnings are effectively a chunk of cash in the business bank account, or they get turned into other assets that go on the balance sheet.
The retained earnings on a balance sheet represent the profits made (or, in the case of a negative balance, the losses) by the company that are not distributed to the shareholders. In more practical terms, retained earnings are the profits your company has earned to date, less any dividends or other distributions paid to investors. Retained earnings refer to the residual net income or profit after tax which is not distributed as dividends to the shareholders but is reinvested in the business.
Factors that affect retained earnings Did you get it ⬇️樂 question: To calculate re, the beginning re balance is added to the net income or reduced by a net loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted.